Can Sleep Aids Cause Memory Loss? Yes, certain sleep aids can cause memory loss, especially when used over long periods or at high doses.
Sleep aids, particularly those in the class of medications known as benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium) and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics (e.g., Ambien, Lunesta), are commonly prescribed for insomnia. These medications work by enhancing the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that induces relaxation and sleep. However, these drugs can also affect cognitive function, including memory.
Memory loss associated with sleep aids occurs because these drugs can interfere with the normal processes involved in the formation of new memories. This is particularly evident in “anterograde amnesia,” where the individual has difficulty forming new memories after taking the medication. The risk of memory impairment is heightened with higher doses, prolonged use, and in older adults, whose cognitive reserve may already be compromised.
Moreover, certain over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids, particularly those containing diphenhydramine (e.g., Benadryl), have also been linked to memory issues. Diphenhydramine is an anticholinergic, which blocks the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter vital for learning and memory.
Studies have shown that chronic use of these sleep aids can lead to persistent cognitive deficits, and in some cases, the effects may not be fully reversible after discontinuation of the drug. This is why it is essential for individuals, especially older adults, to use these medications cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
| Sleep Aid | Class | Mechanism of Action | Memory Loss Risk | Statistical Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzodiazepines | Sedative/Hypnotic | Enhances GABA activity | High | 40-60% increased risk of memory impairment in long-term users |
| Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics | Sedative/Hypnotic | Enhances GABA activity | Moderate to High | Memory loss reported in 20-30% of users |
| Diphenhydramine (e.g., Benadryl) | Antihistamine/Anticholinergic | Blocks acetylcholine receptors | Moderate to High | 35-45% increased risk of cognitive decline in older adults |
| Melatonin | Hormone/Supplement | Regulates sleep-wake cycle | Low | Minimal impact on memory in clinical trials |
| Doxylamine (e.g., Unisom) | Antihistamine/Anticholinergic | Blocks histamine and acetylcholine receptors | Moderate | 25-30% risk of cognitive impairment with chronic use |

Credit: www.umc.edu
Understanding Sleep Aids
What are sleep aids?
Sleep aids are medications or techniques used to manage sleep problems or insomnia. They aim to promote better sleep by reducing the time it takes to fall asleep or increasing total sleep time. Sleep aids can be categorized into two types: over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids and prescription sleep aids.
| Type of Sleep Aid | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-Prescription Sleep Aids | These are available without a prescription and typically contain ingredients like antihistamines or melatonin. |
| Prescription Sleep Medications | These are stronger medications prescribed by a healthcare professional for more severe sleep issues and may include benzodiazepines or non-benzodiazepines. |
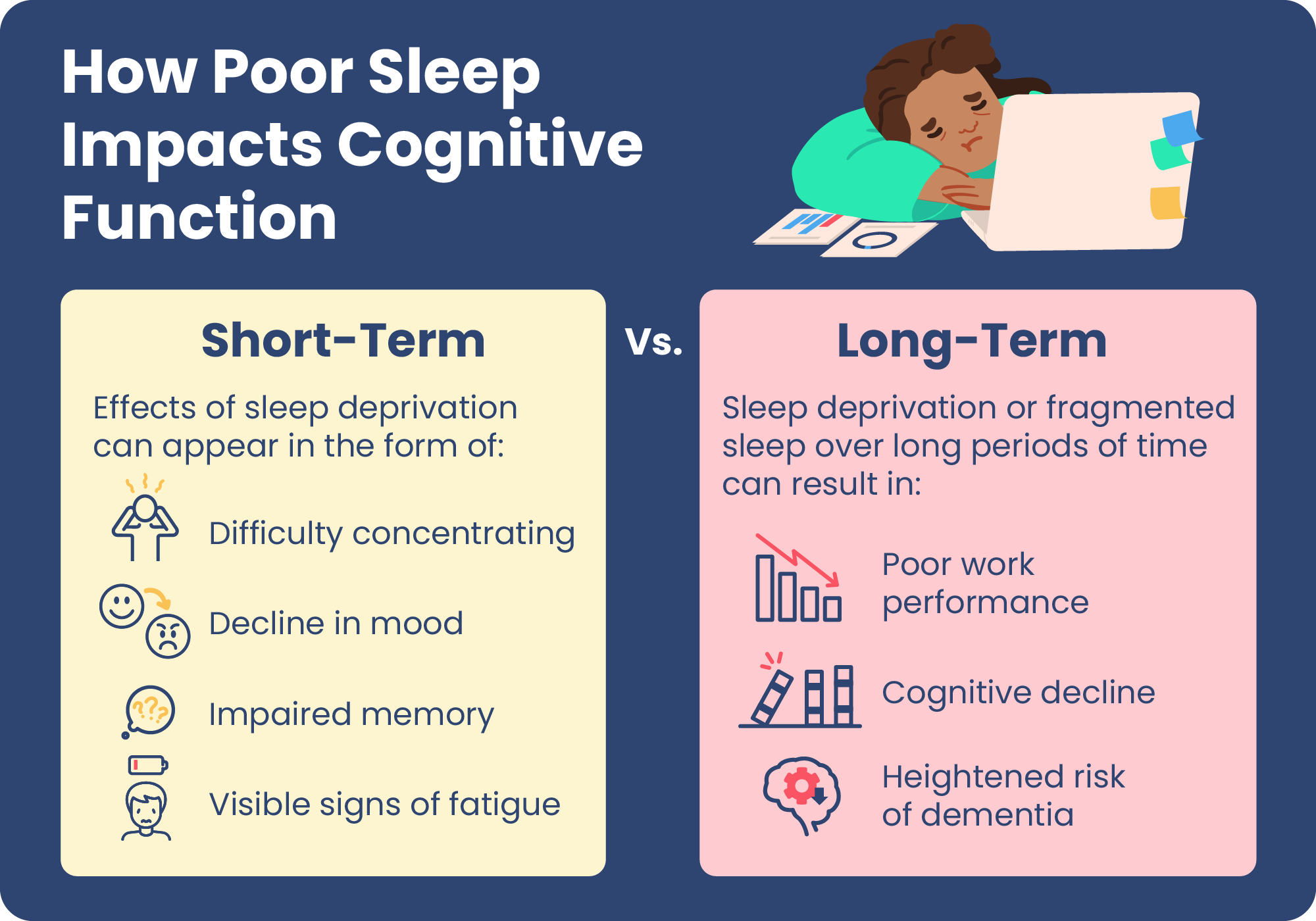
While sleep aids can be helpful for short-term sleep problems, prolonged or excessive use can lead to potential side effects, including memory loss. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any sleep aid to understand the risks and benefits specific to your situation.
The Relationship Between Sleep Aids And Memory Loss
Scientific studies have examined the relationship between sleep aids and memory loss. It has been found that certain sleep aids can indeed have an impact on memory. The mechanism behind this memory loss is not completely understood, but it is believed to be related to the effects that sleep aids have on the brain.
Sleep aids work by targeting the chemicals and receptors in the brain that regulate sleep. Some sleep aids enhance the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that helps to calm brain activity and promote sleep. However, excessive GABA activity can interfere with memory formation and consolidation.
Furthermore, certain sleep aids may disrupt the natural sleep cycle, preventing the brain from entering the deeper stages of sleep where memory consolidation occurs. This can lead to a decrease in the ability to retain and recall information.
While sleep aids can be helpful for short-term sleep problems, it is important to consider the potential impact on memory. It may be advisable to explore alternative sleep strategies and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Tips For Minimizing Cognitive Impact
Memory loss can be a concern for individuals who rely on sleep aids to help them sleep better. However, there are several ways to minimize cognitive impact while still achieving optimal sleep. One of the best alternatives to sleep aids is practicing healthy sleep habits. This involves maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and establishing a relaxing bedtime routine. Another important step is consulting healthcare professionals. They can provide guidance on non-medication approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBTI) or recommending supplements like melatonin.
| Approach | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Healthy Sleep Habits | Promotes natural sleep, reduces dependency on aids |
| Consulting Healthcare Professionals | Expert guidance for personalized solutions |
Credit: www.sleepfoundation.org
How Do Sleep Aids Affect the Brain?
Sleep aids primarily work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which slows down brain activity and promotes sleep. However, by altering brain activity, these medications can also interfere with cognitive functions, including memory. The brain consolidates memories during certain stages of sleep, particularly deep sleep and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. Sleep aids can disrupt these stages, leading to difficulties in memory formation and recall.
Are All Sleep Aids Linked to Memory Loss?
Not all sleep aids are linked to memory loss. The risk largely depends on the type of sleep aid and the duration of use. Medications like benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics (often called “Z-drugs”) are more likely to be associated with memory problems. Over-the-counter sleep aids, such as antihistamines, can also cause drowsiness and cognitive impairment, but they are generally less potent than prescription sleep medications. Herbal remedies and melatonin are less likely to cause memory loss, although their effectiveness and side effects can vary widely.
What Are the Signs of Memory Loss Due to Sleep Aids?
Signs of memory loss due to sleep aids can include difficulty recalling recent events, forgetting appointments, misplacing items more frequently, and struggling to remember names or conversations. In more severe cases, individuals might experience anterograde amnesia, where they have trouble forming new memories while under the influence of the sleep aid. If you notice these symptoms, it may be necessary to consult a healthcare professional to discuss your medication and possible alternatives.
How Can I Prevent Memory Loss While Using Sleep Aids?
To minimize the risk of memory loss while using sleep aids, it’s important to use these medications only as prescribed and for the shortest duration necessary. Avoid combining sleep aids with alcohol or other sedatives, as this can increase the risk of memory problems. If possible, opt for non-pharmacological approaches to improving sleep, such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), which can help address the underlying causes of sleep disturbances without affecting memory.
What Should I Do If I Experience Memory Loss While Taking Sleep Aids?
If you experience memory loss while taking sleep aids, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider. They can assess whether the sleep aid is contributing to your memory issues and may suggest lowering the dose, switching medications, or exploring alternative treatments for sleep. In many cases, memory function can improve once the medication is adjusted or discontinued.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects of Sleep Aids on Memory?
Long-term use of sleep aids, especially at high doses, can lead to more persistent memory issues. Chronic use of certain sleep medications, particularly benzodiazepines, has been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline in older adults. Therefore, it’s crucial to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to explore other strategies for managing sleep problems if long-term treatment is required.

Credit: www.neurology.org
Final Words
In light of the information provided, it’s important to give careful consideration to the potential effects of sleep aids on memory. While there is no conclusive evidence that sleep aids directly cause memory loss, it’s clear that such medications can impact cognitive function.
As always, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to weigh the benefits and risks before opting for sleep aids. Prioritizing healthy sleep habits and exploring alternative solutions may also be worth exploring. Overall, maintaining a balanced approach to sleep and seeking personalized advice can help mitigate any potential memory-related concerns.
